Calculation of Cube Volume
Table of Contents
Volume of a Cube
The volume of a cube is the total space that can fit in this 3D shape. The cube has 6 faces/sides altogether, which all have the same surface area. The derivation of the cube volume formula is shown below.
An example in reality of needing to know the volume, is filling up water tanks, or volume of oil to put in your car engine, or volume of ingredients when cooking a meal. There are examples at the bottom of the page with different units.
This is a common exam question on any mathematics paper and you’ll always need to know this whether you are in high school or studying engineering.
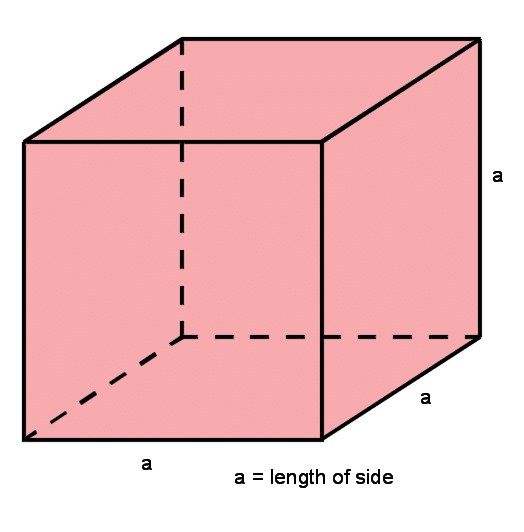
All lengths of the cubes are the same.
The length of each side is a.
The length = a
The width = a
The height = a
Volume = Length x Breadth x Height (which is a3).
Formula for volume of a cube = \(a^3\)
Volume of a Cube Example 1
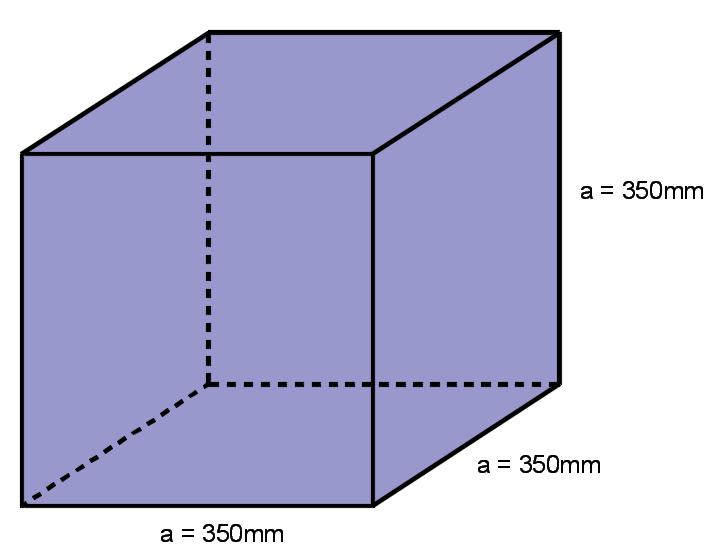
A square box has a length of 350mm, height of 350mm and width of 350mm. Find the volume of the box.
Solution:
The formula for volume of a cube is a3
a = 350 mm
The volume is = (350)3 = 42,875,000 mm3
This can also be written as 0.042875 m3 (42,875,000 multiplied by 10-9 to convert from mm3 to m3).
Note – remember to check units when calculating the surface area.
Volume of a Cube Example 2
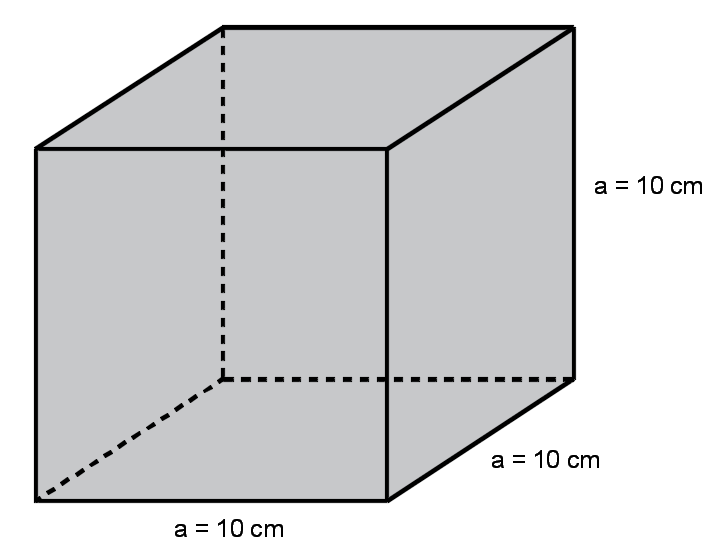
A cube has a length of 10 cm, height of 10 cm and width of 10 cm. Find the volume?
Solution:
The formula for volume of a cube is a3
a = 10 cm
The volume is = (10)3 = 1000 cm3
This can also be written as 0.001 m3 (1000 multiplied by 10-6 to convert from cm3 to m3).
Note – remember to check units when calculating the surface area.
Note – Don’t always assume the shape is a cube in your exams or in a real life application, we need to measure and check the shape before we start any calculations.
