Concrete Foundation Design Procedure
Table of Contents
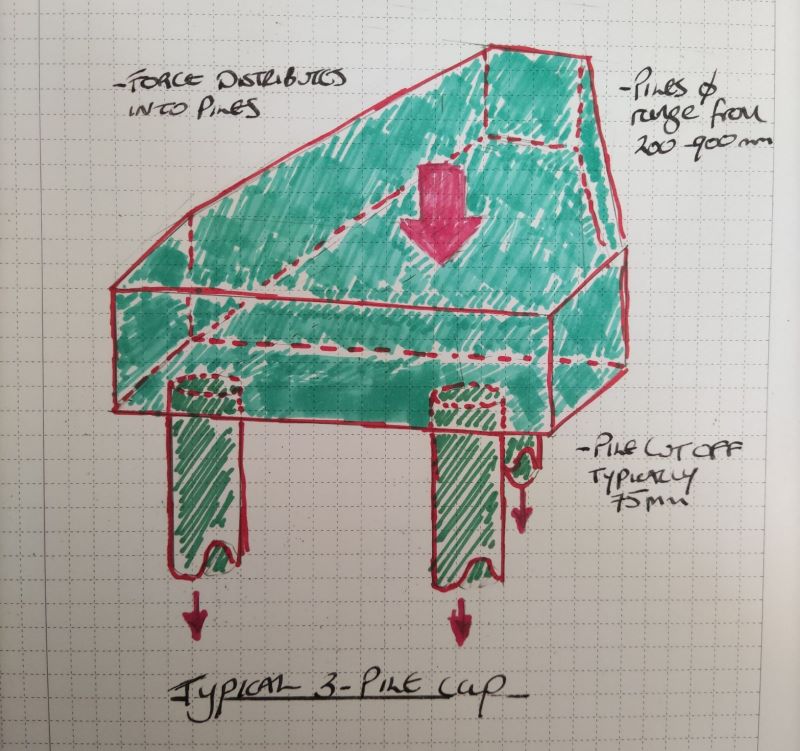
What is a Pile cap?
A pile cap is a substructure foundation which supports internal columns and walls of a building or bridge supports. The purpose of a pile cap is to distribute the internal axial load into piles, which then transfer into competent ground. The forces are generally distributed equally into the piles, but piles are not always installed in the correct place, and tolerances are needed.
Pile caps are a reinforced concrete structure are made using concrete mixes (cement, water and aggregates. The caps are made on site through the use of formwork and shuttering, which forms the shape of the pile cap. Wet concrete is poured into the formwork, and the mixture is then vibrated (using a vibrating rod) before setting and hardening.
An issue can arise from large piled bases where the concrete at the bottom of the cap might begin setting before the rest of the cap, causing cracking and weakening in the concrete section.
Large buildings, high rise buildings and large bridges, which have high column loads require foundations that can distribute these loads into competent ground. The top ground strata are generally inadequate and require deep foundations Types of Pile Foundations (pile foundations) to transfer loads into the ground.
There are construction sites, which have lots of constraints and difficult locations to access. For instance, on a new site, there could be buried structures which mean that piles themselves cannot be positioned as designed by the engineer. The pile itself can be repositioned in the pile cap itself, but this mean there will not be an equal distribution of forces and will cause eccentricity, resulting in additional moments which needs to be designed against in the form of additional reinforcement.
A common ground obstruction is basements and concrete floors, which are sometimes missed when the ground is checked prior to construction but are only discovered when the site is excavated. This causes changes in the foundation setting out, planning and cause delays depending on how significant the changes are.
In addition, there are existing buildings which are renovated, and the function of internal rooms are changed, but require new foundations to support the increase of loading. Internal mini piles can be installed to form a new foundation and the ground slab can be thickened and act as a pile cap.
However, installing new pile caps into existing buildings requires the new and existing foundations to be stitches together (i.e, not a monolithic structure anymore) using dowels/shear connections.
Types of Pile Cap Foundations
There are different types of pile caps:
- 2 pile caps
- 3 pile caps
- 4 pile caps
- 5 pile caps
- Large piled bases
The number of piles required to support an internal column/wall/support depends on the magnitude of the load.
The SLS load of the column/support is checked against the pile capacity when determining the number of piles required.
An example of determining the number of piles is below:
Internal of column SLS load is 2500 kN, and the piles have a pile capacity of 1000 kN.
2500 / 1000 = 2.5. Therefore, a 3 pile cap is required.
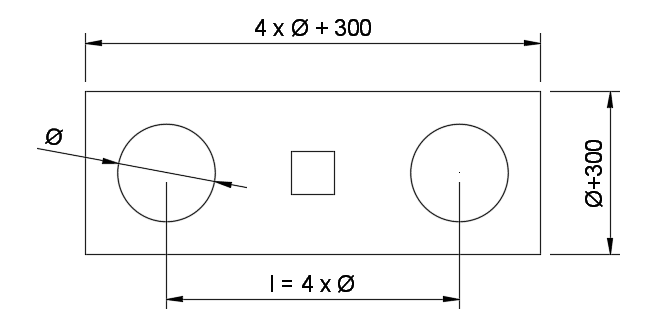
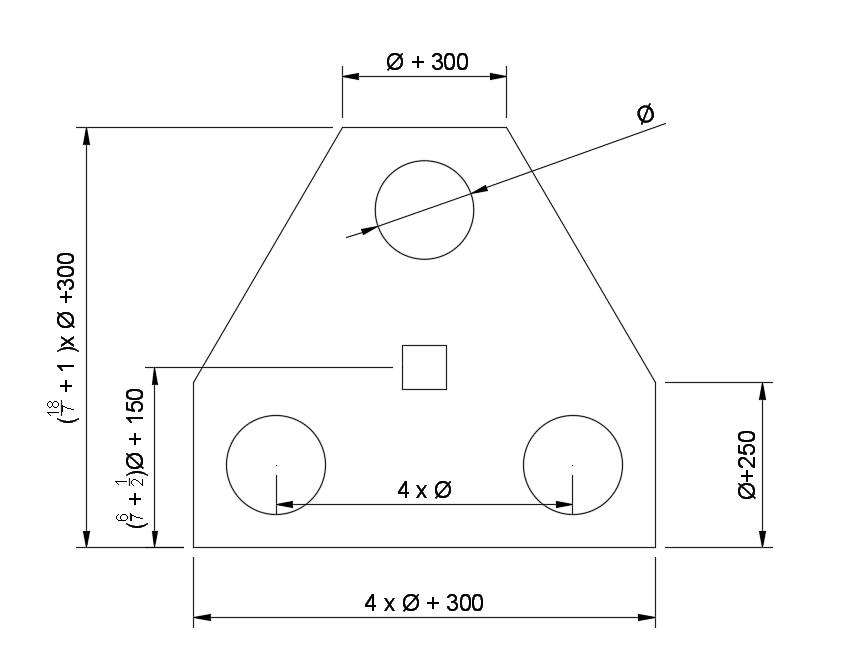
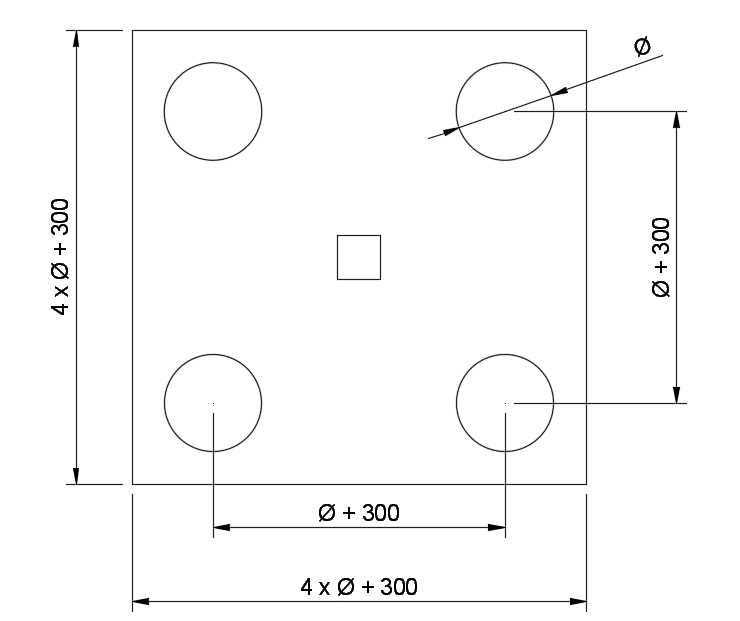
Depths of pile caps
The normal minimum depth of pile caps is generally 600mm.
Pile caps range from 600mm to 2000mm, but that depends of the design and site constraints.
It is important to consider the depth of a pile cap when accounting for the anchorage of column reinforcement and pile reinforcement into the pile cap.
Pile caps are designed and checked against bending moment, shear force, pile punching shear. However, it is common to design pile caps to avoid the use of shear links and shear rails, due to the difficulty in fabricating shear reinforcing and forming cages for large bases. This can be overcome by increasing the depth of the cap, which increases the section size and shear resistance.
Design of Pile caps
The steps to design a pile cap are below:
- Determine load take down into cap
- Determine the size of pile cap (plan and depth)
- Design required reinforcement through beam theory or truss analogy.
- Design reinforcement for bending moments
- Design and check for shear force along shear plane
- Design and check for punching shear
- Draw reinforcement drawing for detailing
Once piles start exceeding 4 piles, using 5 or more piles and large bases, FEA modelling of the base can be used to determine the load take down and pile reactions.
FEA is useful when checking large irregular pile caps due to ground obstructions causing eccentricity in the base or large bases supporting shear cores.
