Calculation of Cone Surface Area
Table of Contents
Surface Area of a Cone
A cone is a 3-D structure which has one flat end, and one curved side shown in the example below. The pointed end of a cone is called the apex and the flat end is called the base. The surface area of a cone is the sum of the flat end and side surface areas.
We have different types of cones such as a right angled cone (this is the example in calculations below) and oblique cone (vertex is away from the center of the base).
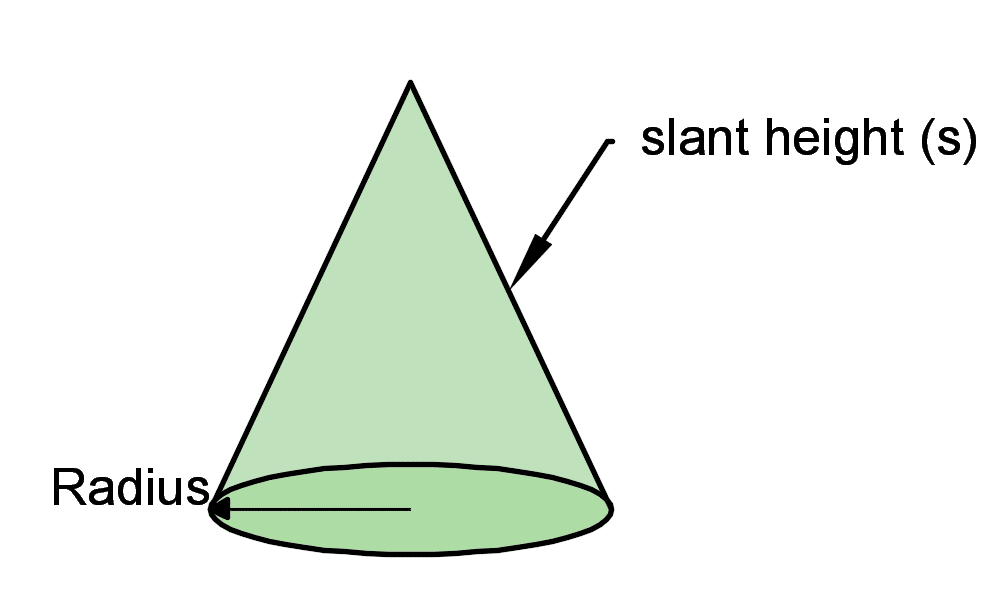
A cone is made up of one curved side and base (circular base). This right angled cone has the apex (tip/point) perpendicular to the base (we can draw a straight line to the center of the flat base)
The area of the base will be πr2 (area of circle).
The surface area of the curved side is π*r*s.
The total surface area of the cone will be πr2 + π*r*s.
r = radius and s = slant height
Formula for Surface area of a Cone = πr2 + π*r*s.
Surface Area of a Cone Example 1
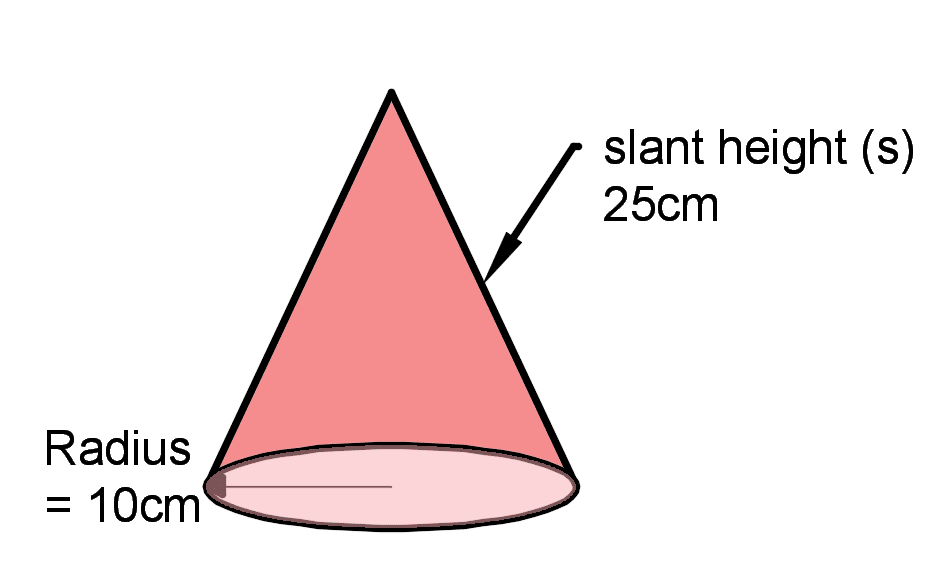
A cone has radius of 10 cm at the base and a slant height of 25 cm. What is the surface area of the cone?
Solution:
The surface area of a cone formula is πr2 + π*r*s.
Surface area = (π*102) + (π*10*25) = 1100 cm2
This can also be written as 0.11 m2 (1100 multiplied by 10-4 to convert from cm2 to m2).
Note – remember to check units when calculating the surface area.
Surface Area of a Cone Example 2
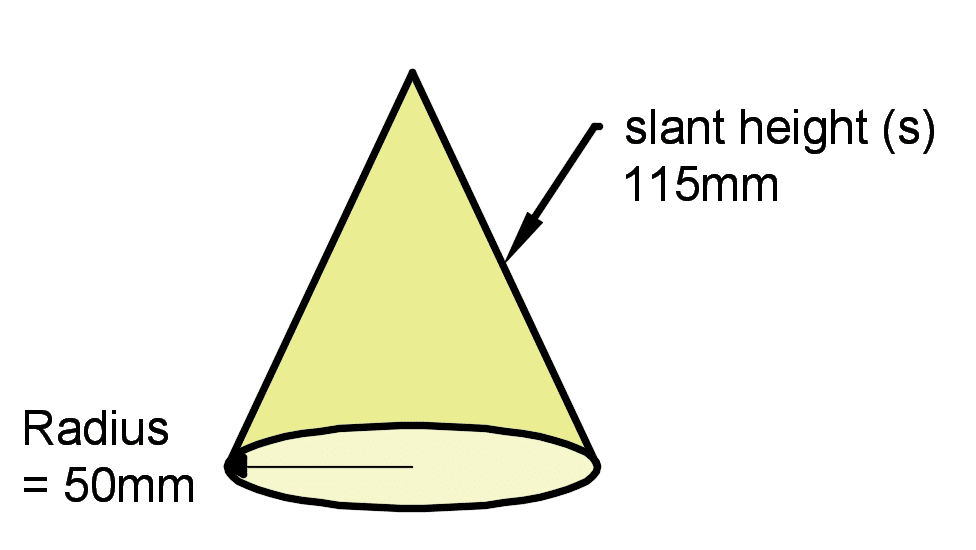
A cone has radius of 50 mm at the base and a slant height of 115 mm. What is the surface area of the cone?
Solution:
The surface area of a cone equation is πr2 + π*r*s.
Surface area = (π*502) + (π*50*115) = 25920 mm2
This can also be written as 0.0259 m2 (25,920 multiplied by 10-6 to convert from mm2 to m2).
Note – remember to check units when calculating the surface area.
