Types of Engineering
Table of Contents
Civil Engineering Sub-disciplines
Civil engineering is a very broad field with lots of sub-disciplines. The term “Civil Engineer” could apply to anyone working as a site engineer, or an engineer designing housing, pavements, drainage, dams and surveying construction sites. However, they will all apply principles of structural engineering, nontechnical engineering or construction engineering depending on what project they work on and the size of the project.

Earthquake engineering
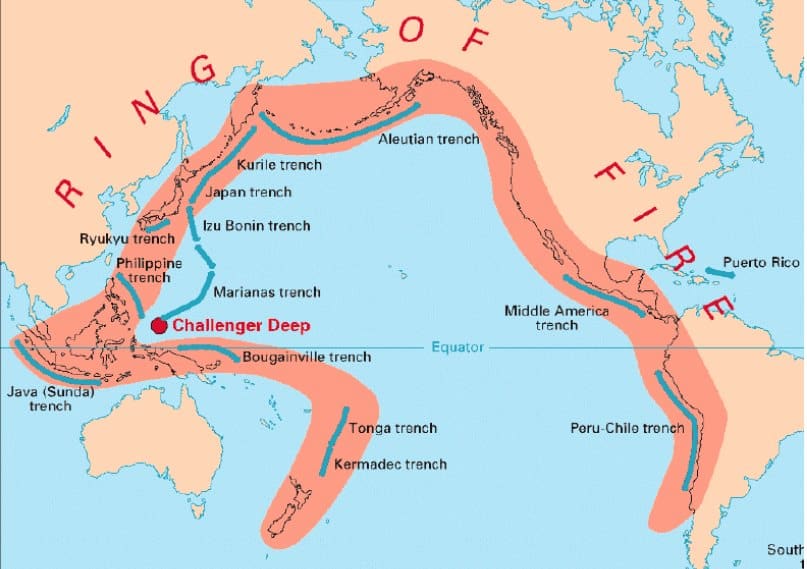
Earthquake engineers are involved with designing structures in earthquake prone zones. Earthquakes frequently happen in locations of tectonic plates (95% of all earthquakes happen near plate boundaries). This forces engineers to consider the consequences of seismic activity; i.e, when the ground is shaking and liquefaction occurs, buildings and their foundations need to be able to resist these actions without collapsing. Countries that are frequently affected are USA, Japan, Turkey, Indonesia, or any country that sits within the ring of fire.
Coastal Engineering
Coastal engineers are involved in designing sea defenses and coastal protection measures against flooding and erosion. This is can be achieved via hard or soft engineering to designs. Countries that are at risk of loosing land due to rising water levels and man-made diversions of rivers and hard engineering techniques are Bangladesh, United Kingdom and many others.
When an ecosystem is affected by man-made buildings or river diversions, there will always be unforeseen consequences, which is usually to late to stop or the damage may have already been done.
Hard engineering is likes of sea walls, groynes, and Gabian walls. Soft engineering involves afforestation of coastal dunes, beach stabilization, beach nourishment (make a beach using sand and shingles).
Geo-techinical Engineering
Geo-technical engineering involves the study of geology and rock formations to for the design of engineering systems. The theory of soil science, mechanics is used to design structures such as retaining walls, foundations such as pads, rafts and piles.
Also, it is difficult to predict the properties and behavior of soil due to limited testing, so large factors of safety are commonly used in geo-technical designs.
Geo-techinical engineers frequently carry out investigations such as measuring ground gas, assessing the strength of soil via shear vane tests or tri-axial load tests and many more types of investigation.

Structural Engineering
Structural engineering involves the design of building , bridges, towers, offshore gas fields and airports. Structural engineering is quite diverse it itself, but whether you need a structure built, there should be a structural engineer overlooking the design.
Their role involves the structural analysis of the structure to be designed via FEA software’s such as Tekla structural designer, Scia Engineer (There are many other software’s out there).
These software’s analyse the loads applied to a structure and analyses the applied stress and determines whether it is adequate.
For example, a floor beam will undertake its self-weight (permanent), weight of floor system (permanent – could be timber or concrete or composite deck) and the weight of occupants (Variable load). The sofware will then analyse this against all relevant code checks and the output has to be checked by the structural engineer.
Also, structural engineers have to consider the stability of the structure, any wind or seismic loading and temporary load conditions. They will also be closely involved with site engineers to help develop the construction strategy and highlight areas of significant risks.

Transportation Engineering
Civil engineering disciplines such as transportation or Highway engineering are involved in the design and development of road and highway systems. They are involved in planning and conception stages in new developments but also need to determine the road types required, road and pavement buildup and whether it has adequate capacity.
They are also heavily involved with local councils and shareholders in driving projects but also private landowners if a road needs to be built on someones private property (i.e, farmland).
A well-know example which is being developed in the United Kingdom is the Smart motorway scheme being developed by Highway England, which uses active traffic management systems to control the flow of traffic via variable speed limits and other means.
Water/waste-water engineering
Civil Engineers in the water industry are involved in planning and developing new drainage utilities and infrastructure. These kinds of designs include the design of new pipes feeding fresh water into homes, commercial areas and transporting waste-water away from site.
They will generally closely with other disciplines such as structural engineers and transport engineer as a lot of co-ordination is required when developing a new construction site or renovating an existing building.
Civil engineering is very broad, but these sub-disciplines closely work together to bring projects and innovative concepts to life. Many engineers themselves move between disciplines once they have gained enough experience.
