Masonry Properties
Table of Contents
Typical Brick Sizes
This article details information on the size of bricks (detailed dimensions) that are commonly used in the UK. There are many different brick types and the sizes change depending on the country of manufacture. It is important to get the brick size correct when undertaking any detailed design.
The size of a standard brick in the UK is 215mm x 102.5mm x 65mm (length x depth x height). Blockwork dimensions are 440mm ( varies) x 215mm (length x depth x height).
In current times, the special shaped bricks are becoming more common. This is because of its aesthetic benefits that architects prefer. These types of bricks are much more readily available to manufacture and design than they once were in the past, due to manufacturing advancements.
It is important to consider the overall wall dimensions when using bricks on site to minimise cutting on site, and any other potential problems (i.e, it is easier to set the height of the wall based on the brick coursing – you don’t want to cut half a brick).
Another aspect to consider are areas around windows and door openings, and making sure they are correctly set out (i.e, brick size and depth of mortar will impact overall dimensions). Lintels with brick slips are a common element, which are used and specified above door frames and windows.
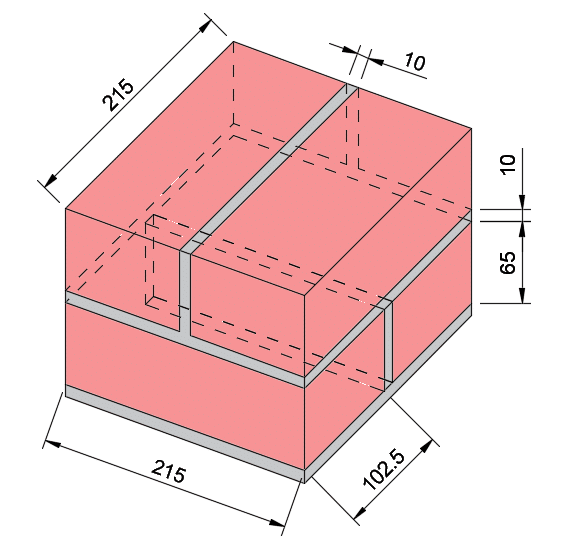
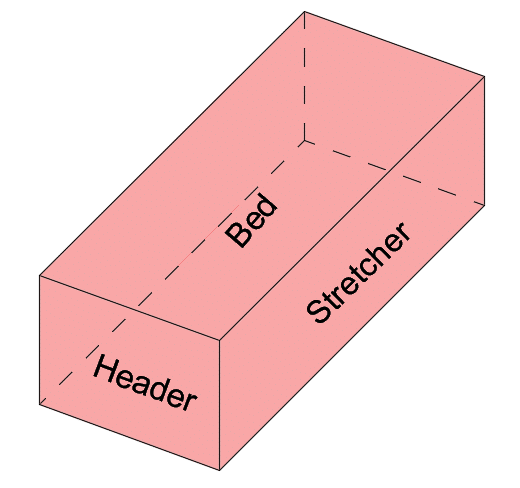
Other Typical Brick Sizes
| Standard | Imperial (in) | Metric (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Australia | 9 x 4\(\frac{1}{3}\) x 3 | 230 x 110 x 76 |
| Denmark | 9 x 4\(\frac{1}{4}\) x 2\(\frac{1}{4}\) | 228 x 108 x 54 |
| Germany | 9 x 4\(\frac{1}{4}\) x 2\(\frac{3}{4}\) | 240 x 115 x 71 |
| India | 9 x 4\(\frac{1}{4}\) x 2\(\frac{3}{4}\) | 228 x 107 x 69 |
| Romania | 9 x 4\(\frac{1}{4}\) x 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) | 240 x 115 x 63 |
| Russia | 10 x 4\(\frac{3}{4}\) x 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) | 250 x 120 x 65 |
| South Africa | 8\(\frac{3}{4}\) x 4 x 3 | 222 x 106 x 73 |
| Sweden | 10 x 4\(\frac{3}{4}\) x 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) | 250 x 120 x 62 |
| United Kingdom | 8\(\frac{3}{4}\) x 4 x 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) | 250 x 120 x 65 |
| United States | 7\(\frac{5}{8}\) x 3\(\frac{5}{8}\) x 2\(\frac{1}{4}\) | 194 x 92 x 57 |
Engineering brick properties
There are two engineering brick classes, class A and B. These bricks have high compressive strength and low water absorption.
Class A engineering bricks has a compressive strength greater than 70 N/mm2 and a water absorption less than 4.5%. Class B engineering bricks have to achieve a compressive strength in excess of 70 N/mm2 and a water absorption less than 7 per cent. Engineering brick sizes are 215mm x 102.5mm x 65mm.
The typical density of clay bricks range from 22 – 28 kN/m2
Mortar Properties
Mortar is a very old building material that is used as a bonding agent between bricks. It is made using aggregate, binder and water and the property of the mortar changes depending on the type of binder and aggregate used in the design mix.
It is important to consider brick sizes and the bonding arrangement of the masonry wall when looking at the design of masonry as well as mortar properties.
The following mortar types are listed below:
- Fire-resistant mortar/ firestop mortar – Mortar made using cement mixed with powdered fire bricks to create a fireproofing agent.
- Sound absorbent mortar
- X-ray mortar – high density mortar used to block X-ray radiation.
- Chemical resistant mortar
- Lightweight mortar – Bulk density less than 15 kN/m3
- Heavy mortar – Bulk density of mortar greater than 15 kN/m3
This table can be found in BS EN 1996-1:2005. Table NA.2.
| Compressive Strength class | Compressive strength fm | Mortar class | Mortar constituents and proportions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement:Lime:Sand | Cement:Sand | Masonry Cementa:Sand | Masonry Cementb:Sand | |||
| M12 | 12 N/mm2 | (i) | 1:0:3 to 1:\(\frac{1}{4}\):3 | 1:3 | ||
| M6 | 6 N/mm2 | (ii) | 1:\(\frac{1}{2}\):4 to 1:\(\frac{1}{2}\):4\(\frac{1}{2}\) | 1:3 to 1:4 | 1:2\(\frac{1}{2}\) to 1:3\(\frac{1}{2}\) | 1:3 |
| M4 | 4 N/mm2 | (iii) | 1:1:5 to 1:1:6 | 1:5 to 1:6 | 1:4 to 1:5 | 1:3\(\frac{1}{3}\) to 1:4 |
| M2 | 2 N/mm2 | (iv) | 1:1:8 to 1:1:9 | 1:7 to 1:8 | 1:5\(\frac{1}{2}\) to 1:6\(\frac{1}{2}\) | 1:4\(\frac{1}{2}\) |
(a) Sulphate resisting mortar is advised where soluble sulphates are expected from the ground, saturated bricks or elsewhere.
(b) F indicates that the bricks are frost resistant, M indicates moderate frost resistance and 0 indicates no frost resistance.
(c) N indicates thatthe bricks have normal soluble salt content and L indicates low soluble salt content.
(d) Retaining walls planter boxes should waterproofed on their retaining faces to improve durability and prevent staining.
